One of the most captivating trends to have appeared in the last few years has been the rise of “alternative meats.” With more diners choosing to leave animal meat out of their meal choices – whether it is for health, ethical, or environmental reasons – this is the perfect time for restaurants to include “alternative meats” into their dishes and menus.
And your choice of alternative meats comes down to two broad categories – plant-based meat or lab-grown meat.
What are some differences between plant-based meat vs lab-grown meat, and which meat alternative is better? Keep on reading to find out!

Plant-based meat
Plant-based meat is not a new concept. After all, veggie burgers have been around for decades. But while veggie burgers were created as a vegetarian and vegan option, veggie patties don’t really taste like beef, chicken, or pork. On the other hand, plant-based meats are rapidly gaining popularity even amongst meat eaters because they taste just like animal meat.
So, how are plant-based meats created? There are several methods, but the most popular technique is known as the “high-moisture extrusion”. Plant-proteins are put inside a barrel before going through thermal and mechanical stresses – a process that involves a variety of heating, cooling, and shearing techniques – to produce a product that is essentially plant proteins with a meat-like texture. By altering the texture process slightly, the characteristics of each plant-based meat can also be changed.
These meat-like plant proteins are now ready to be made into ‘meat products’, much like UFS’s The Vegetarian Butcher noChicken Burger patties, and NoMeatball meatballs. These plant-based meat products are then ready for restaurants to use, either to create brand-new recipes or to conjure up a special “meatless” version of an existing (and usually highly popular) dish.
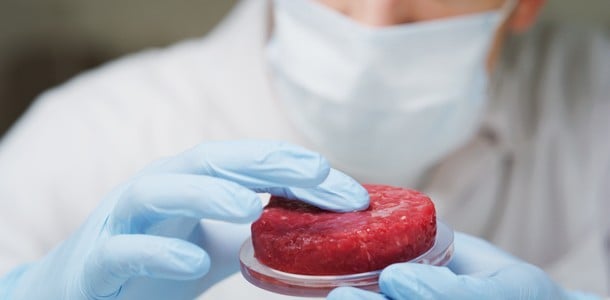
Lab-grown meat
Also known as “cultured meat”, lab-grown meat takes on a different approach to creating ‘alternative’ meats. Lab-grown meat uses muscle samples and stem cells from animals, then cultivates (i.e., grows) this small sample into a large amount of meat.
Unlike plant-based meat that is made from soya or other non-meat ingredients, lab-grown meat contains the exact same nutrition and animal protein as conventionally produced beef, pork, or chicken.1 This allows diners the option of eating real meat without having to worry about ethical or environmental concerns.
As lab-grown meat is animal meat, it may not be suitable for consumers who have certain health concerns, or diners who are avoiding meat due to religious beliefs.

Which is better: plant-based meat vs lab-grown meat
At present, plant-based meats are starting to play an increasingly important role in restaurant menus – especially as chefs are looking to create dishes that appeal to the expanding numbers of flexitarian diners across the country.
However, the cost of producing lab-grown meat is significantly higher, and as such, is not widely available or affordable for most restaurants. As lab-grown meats become more affordable, these too, could share a space on dining tables.
Both plant-based meat and lab-grown meat offer their own benefits. While some diners may be interested in trying the latter, cultivated meat may make its way to restaurant menus at a much slower pace. In the meantime, be sure to experiment with your ingredients and incorporate plant-based meats into your popular dishes. This way, you can encourage your diners to step out of their comfort zone and let them discover how tasty meat alternative dishes can be!

Recipe eBook for Flexitarians, Vegans, & Vegetarian Diners
Meet the needs of the growing number of plant-based food lovers by creating dishes for them. Get inspired with our recipe ebook and adapt those recipes to suit your diners' tastebuds.